Arthroscopy of pets
What is it?
Advances in human medicine and interest in minimally invasive surgical techniques have led to the use of arthroscopy in veterinary medicine.
The arthroscopic technique allows more precise visualization of the various internal structures.
Arthroscopy provides excellent optical vision through magnification and illumination of internal joint structures. Arthroscopic examination is performed using a rigid endoscope connected to an optical fiber and a light source.
Shoulder and elbow joints
Pathologies of the elbow joint are those for which arthroscopic evaluation is most appropriate. Diagnosis and surgical correction induce minimal trauma to the joint and surrounding structures.
The shoulder joint is another area where arthroscopy is proving an effective diagnostic and curative method. Fragmentation of the medial coronoid process (FPCM) is a commonly treated pathology, as is Osteochondritis Dissecans (OCD), which is frequently diagnosed in large-breed dogs. These lesions may be invisible on X-ray, and can be treated using the arthoscope, often after diagnosis with 3D reconstruction imaging (CT scan).
High-resolution interface
We use the latest-generation endoscopy/arthroscopy column for superior image quality, and equipment such as VAPR VUE (radiofrequency electrode-generated plasma vaporization) for minimally invasive treatment.
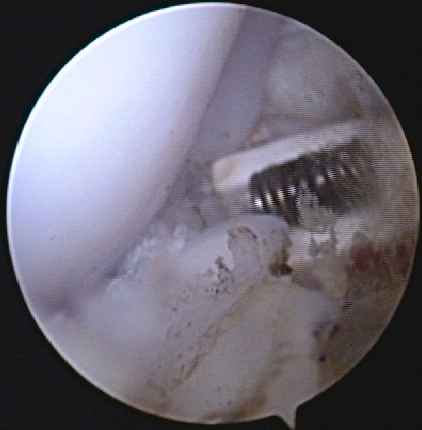
Australien Arthroscopy of the knee for ligament prosthesis in an Australian Shepherd Dog
Advantages
→ Highly precise joint biopsy technique
→ Diagnosis of non-bone pathologies (joint, ligament, tendon, etc.)
→ Good post-operative recovery
→ Technically minimally invasive
→ Video and photo recording
Knee joint
Today, we offer arthroscopic treatment of a wide range of knee pathologies, including :
- Treatment of meniscus injuries
- Minimally invasive arthroscopic replacement of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) following rupture with a ligament prosthesis (NOVETECH)
